Unlocking Web Security: Why HTTPS Is Your Digital Shield
In an increasingly interconnected world, where every click, every search, and every download leaves a digital trace, understanding the fundamentals of online security is no longer optional—it's essential. You might be accessing a simple video like "https qu ax txvtq mp4" or managing sensitive financial data, but the underlying protocols that protect your information remain paramount. This article delves deep into the critical role of HTTPS, explaining why it's the bedrock of secure communication over a computer network and how it safeguards your privacy in the vast expanse of the internet.
Have you ever wondered why a lock icon appears on your browser URL bar? And why is it important? We did too, and this comprehensive guide is for you. From the basic handshake between your browser and a website to the intricate encryption mechanisms that keep your data private, we'll unravel the complexities of HTTPS, making it accessible and understandable for everyone. Prepare to gain expertise on how this vital protocol works, why it's widely adopted, and what it means for your everyday online interactions, ensuring your digital journey is both safe and secure.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is HTTPS? The Foundation of Secure Web Communication
- Why HTTPS is Crucial: Protecting Your Data in a Connected World
- How HTTPS Works: Demystifying TLS Encryption
- The Browser Lock Icon Explained: Your Visual Cue for Security
- HTTPS and Your Digital Footprint: Google Analytics, Microsoft Accounts, and Beyond
- Implementing HTTPS for Websites: A Must for Trust and SEO
- The Future of Secure Web Browsing: Evolving Standards and Threats
- Beyond the Basics: Advanced Security Measures and Best Practices
What Exactly is HTTPS? The Foundation of Secure Web Communication
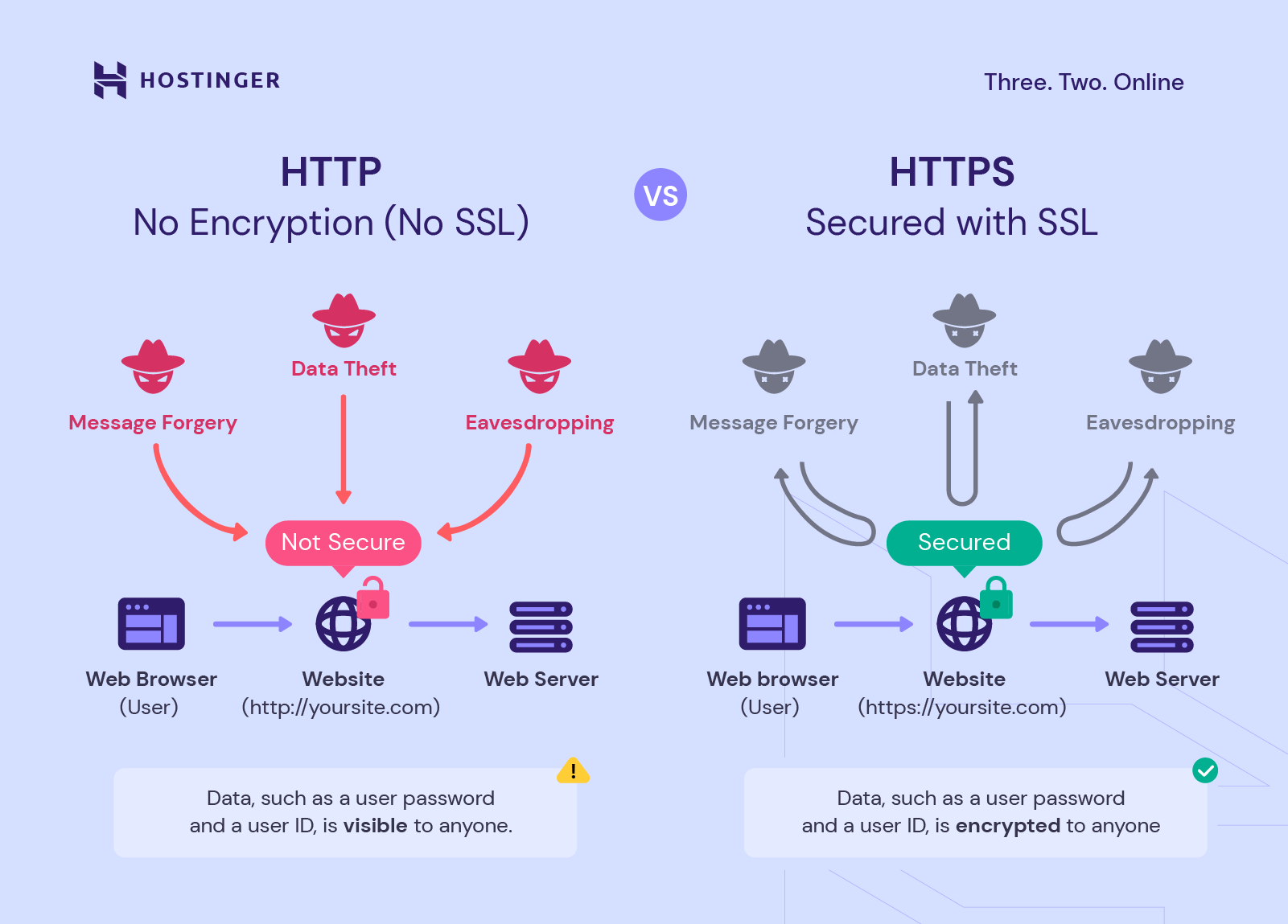
At its core, HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. It is the most common protocol for sending data between a web browser and a website, but with a critical enhancement: security. Unlike its predecessor, HTTP, HTTPS employs encryption for secure communication over a computer network, making it widely adopted across the internet. When you type a web address into your browser, whether it's for a social media site, an online store, or even to access a file like "https qu ax txvtq mp4", your browser initiates a connection. If that connection begins with "https://", it means the data exchanged between your browser and the website is encrypted.
This encryption is vital because it prevents unauthorized third parties from intercepting and reading your data as it travels across the internet. Imagine sending a postcard versus a sealed letter. HTTP is like sending a postcard; anyone can read the message. HTTPS is like sending a sealed, encrypted letter; only the intended recipient with the correct key can decipher its contents. This fundamental difference is why HTTPS has become the industry standard for any website that handles sensitive information, from login credentials and payment details to personal messages and private documents.
The widespread adoption of HTTPS isn't just about protecting individual users; it's also about building a more trustworthy and resilient internet. Search engines like Google actively favor HTTPS-enabled websites, not only for security reasons but also as a ranking signal. This push from major tech companies has accelerated the transition from HTTP to HTTPS, making secure browsing the default experience for most internet users today. Understanding this foundational element is the first step in appreciating the complexities and benefits of modern web security.
Why HTTPS is Crucial: Protecting Your Data in a Connected World
The importance of HTTPS cannot be overstated in today's digital landscape. Its primary function is to provide three essential layers of protection: encryption, data integrity, and authentication. Without these safeguards, every piece of information you send or receive online would be vulnerable to interception and manipulation.
- Encryption: This is the most widely recognized benefit. When a user connects to a webpage via HTTPS, all communication between the client (your browser) and the server (the website's host) is encrypted. This means that if an attacker were to intercept the data, they would only see scrambled, unreadable text. This protects sensitive information like credit card numbers, passwords, personal identification, and even your browsing history from eavesdroppers. For instance, if you were to stream a private video file, say "https qu ax txvtq mp4", over an insecure HTTP connection, anyone on the same network could potentially see what you're watching. With HTTPS, that information is private.
- Data Integrity: HTTPS ensures that the data sent between your browser and the server has not been tampered with during transit. It uses cryptographic checks to detect any unauthorized alteration of the data. If even a single character is changed, the integrity check will fail, alerting the browser that the data is compromised. This prevents malicious actors from injecting malware, advertisements, or false information into the webpage you are viewing.
- Authentication: HTTPS verifies that you are communicating with the legitimate website you intended to visit, not an impostor. This is achieved through digital certificates issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). When your browser connects to an HTTPS site, it checks the site's certificate to confirm its authenticity. This protects against phishing attacks, where malicious websites try to impersonate legitimate ones to steal your credentials.
These three pillars of security are fundamental to maintaining privacy and trust online. Without HTTPS, the internet would be a far more dangerous place, riddled with opportunities for data theft, fraud, and misinformation. The simple lock icon in your browser URL bar is a powerful indicator of these protections at work, signaling that your connection is secure and your data is safe from prying eyes.
How HTTPS Works: Demystifying TLS Encryption
The magic behind HTTPS lies in its use of TLS (Transport Layer Security) encryption. TLS is the successor to SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and is the cryptographic protocol that provides secure communication over a computer network. It sits on top of the HTTP protocol, encrypting all communication between a client and a server. When your browser requests a webpage over HTTPS, a complex series of steps unfolds to establish a secure, encrypted tunnel before any actual data is exchanged.
The TLS Handshake: Establishing Trust
The process begins with what's known as the TLS handshake. This is a crucial initial negotiation between your web browser (the client) and the website's server. Here's a simplified breakdown:
- Client Hello: Your browser sends a "Client Hello" message to the server, indicating its desire to establish a secure connection. This message includes the TLS versions it supports, the cipher suites (encryption algorithms) it can use, and a random string of bytes.
- Server Hello: The server responds with a "Server Hello" message, selecting the best TLS version and cipher suite that both parties support. It also sends its digital certificate, which contains its public key and is verified by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
- Certificate Verification: Your browser verifies the server's certificate. It checks if the certificate is valid, not expired, and issued by a CA it trusts. If the certificate is valid, your browser extracts the server's public key.
- Key Exchange: Using the server's public key (from the certificate), your browser encrypts a pre-master secret and sends it to the server. Only the server, with its corresponding private key, can decrypt this pre-master secret. Both the client and server then use this pre-master secret, along with other random data exchanged earlier, to generate a unique "session key."
- Finished: Both parties send "Finished" messages, encrypted with the newly generated session key, to confirm that the handshake is complete and the secure connection is established.
This entire handshake process typically takes milliseconds, making it virtually imperceptible to the user. Once completed, all subsequent data exchanged during that session is encrypted using the agreed-upon session key.
Data Encryption: The Core of Security
After the TLS handshake, the real work of encryption begins. The session key generated during the handshake is a symmetric key, meaning the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. This makes the process highly efficient for continuous data transfer. Every piece of data, whether it's your login credentials, the content of a webpage, or even a file download like "https qu ax txvtq mp4", is encrypted before it leaves your computer and decrypted upon arrival at the server, and vice-versa. This ensures that even if the data stream is intercepted by a third party, it appears as an unintelligible jumble of characters, rendering it useless to anyone without the correct session key.
The strength of this encryption relies on complex mathematical algorithms and the robust infrastructure of Certificate Authorities. This intricate dance of keys and algorithms is what makes HTTPS a formidable barrier against cyber threats, safeguarding your online activities from start to finish.
The Browser Lock Icon Explained: Your Visual Cue for Security
Have you ever wondered why a lock icon appears on your browser URL bar? This seemingly small detail is actually a powerful visual indicator of your connection's security status, and understanding it is crucial for safe browsing. The lock icon, typically displayed next to the website's address (URL), signifies that the website you are visiting is using HTTPS, meaning your communication with that site is encrypted and secure.
When you see the lock icon, it tells you several important things:
- Encrypted Connection: The data exchanged between your browser and the website is encrypted using TLS. This protects your sensitive information, such as passwords, credit card numbers, and personal details, from being intercepted and read by unauthorized parties.
- Authenticated Website: The website's identity has been verified by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). This helps ensure that you are connecting to the legitimate website you intended to visit, not a fraudulent phishing site attempting to steal your information.
- Data Integrity: The data being transmitted has not been tampered with or altered during transit. This means the content you see on the page is exactly what the website intended to send.
Conversely, if you do not see a lock icon, or if your browser displays a "Not Secure" warning (often accompanied by a broken lock icon or a red line through "HTTPS"), it indicates that the website is using HTTP. In such cases, any information you send or receive is unencrypted and vulnerable to eavesdropping. This is particularly dangerous on public Wi-Fi networks where malicious actors can easily intercept unencrypted traffic. Always exercise extreme caution on "Not Secure" websites, especially when asked to enter personal or financial information.
Major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge have made these visual cues prominent to empower users to make informed decisions about their online safety. Getting into the habit of checking for the lock icon is a simple yet effective step in protecting your digital life. It's your first line of defense against many common online threats, ensuring that your connection to resources, even something as seemingly innocuous as "https qu ax txvtq mp4", is handled with the utmost security.
HTTPS and Your Digital Footprint: Google Analytics, Microsoft Accounts, and Beyond
The impact of HTTPS extends far beyond just securing your browsing sessions; it deeply intertwines with how your digital footprint is managed and how major online services operate. From tracking website performance to managing your personal accounts, HTTPS is an integral part of the secure ecosystem that enables these services to function reliably and privately. Your Google account’s analytics and search console, for instance, heavily rely on secure connections, as do your interactions with services like Microsoft accounts.
Google Analytics & Search Console: The Secure Connection
For website owners and marketers, Google Analytics and Google Search Console are indispensable tools for understanding website traffic, user behavior, and search performance. Both of these platforms require your website to be securely connected via HTTPS for accurate data collection and reporting. Your Google account’s analytics and search console will have to be updated to match your site's HTTPS migration. When your website switches from HTTP to HTTPS, it's not just a change in protocol; it's a fundamental shift in how data is transmitted and perceived by Google's crawlers and tracking scripts.
- Data Accuracy: HTTPS ensures that the data collected by Google Analytics is secure and untampered. This is crucial for accurate insights into user behavior, conversions, and traffic sources.
- SEO Benefits: As mentioned, Google uses HTTPS as a ranking signal. Migrating to HTTPS and ensuring your Search Console is updated helps maintain or improve your search engine visibility. Search Console specifically provides tools to monitor your HTTPS migration, identify issues, and ensure that Google correctly indexes your secure pages.
- Referrer Data: When a user navigates from an HTTPS site to another HTTPS site, the referrer information (the source page) is preserved. If they navigate from an HTTPS site to an HTTP site, the referrer data is often stripped, impacting analytics accuracy. This "secure referrer" policy encourages an all-HTTPS web.
In essence, a secure website is a prerequisite for a healthy and accurately measurable online presence, reinforcing the idea that security isn't just a technical detail but a strategic imperative.
Microsoft Account Security: Managing Settings Securely
Similarly, interacting with major online service providers like Microsoft relies heavily on HTTPS. Whether you're signing in to your Microsoft account to manage your settings, access personalized services like Outlook or OneDrive, or use any of their cloud-based applications, the entire communication is encrypted using HTTPS. This ensures that your login credentials, personal data, and activity within these services remain private and protected from potential eavesdropping.
- Login Protection: When you enter your username and password, HTTPS encrypts this data before it leaves your device, preventing credential theft.
- Session Security: Once logged in, your entire session remains encrypted. This means that even if you're on a public Wi-Fi network, your emails, documents, and other sensitive information within your Microsoft account are protected from snoopers.
- Privacy Settings: Managing your privacy settings, security preferences, and billing information within your Microsoft account is also done over HTTPS, ensuring that these critical configurations are applied securely and confidentially.
The robust implementation of HTTPS by tech giants like Google and Microsoft underscores its foundational role in safeguarding user privacy and maintaining the integrity of personal and business data across vast, interconnected networks. It's a testament to how crucial this protocol is for the smooth and secure functioning of the internet as we know it.
Implementing HTTPS for Websites: A Must for Trust and SEO
For website owners, the transition to HTTPS is no longer optional; it's a fundamental requirement for establishing trust, ensuring data security, and maintaining search engine visibility. The move from HTTP to HTTPS, often referred to as an "SSL/TLS migration," involves several key steps and offers significant benefits that directly impact a website's success.
The primary reason to implement HTTPS is, of course, security. By encrypting all data exchanged, websites protect their users from various threats, including:
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Where attackers intercept communication between a user and a website.
- Eavesdropping: Unauthorized listening to private conversations or data transmissions.
- Data Tampering: Altering data during transit without the user's knowledge.
Beyond security, the benefits extend to user trust and search engine optimization (SEO):
- Enhanced User Trust: The visible lock icon and "Secure" label in browsers immediately signal to users that the site is safe. This builds confidence, particularly for e-commerce sites or those handling sensitive user information. Users are more likely to complete transactions or provide personal data on a site they perceive as secure.
- SEO Ranking Boost: As early as 2014, Google announced that HTTPS would be a lightweight ranking signal. While not the most powerful factor, it contributes to overall SEO performance. In a competitive search landscape, every advantage counts. Furthermore, modern browsers increasingly flag HTTP sites as "Not Secure," which can deter visitors and negatively impact bounce rates, indirectly affecting SEO.
- Access to Modern Browser Features: Many advanced browser features, such as Geolocation, Service Workers (for progressive web apps), and HTTP/2 (which offers performance benefits), require a secure HTTPS context to function. Without HTTPS, websites are locked out of these powerful capabilities.
- Accurate Analytics and Referrer Data: As discussed, HTTPS ensures accurate referrer data is passed between secure sites, providing cleaner and more reliable analytics for site owners.
The process of migrating to HTTPS typically involves obtaining an SSL/TLS certificate from a Certificate Authority, installing it on the web server, and then configuring the website to serve all content over HTTPS, including updating internal links and redirecting old HTTP URLs. While it requires technical effort, the long-term benefits in terms of security, user trust, and SEO make it an indispensable investment for any serious online presence.
The Future of Secure Web Browsing: Evolving Standards and Threats
While HTTPS has become the cornerstone of web security, the digital landscape is constantly evolving, bringing with it new challenges and advancements. The future of secure web browsing will be shaped by ongoing efforts to strengthen encryption, combat emerging threats, and make security more pervasive and seamless for users.
One significant area of development is the evolution of TLS itself. Newer versions, like TLS 1.3, offer improved performance and enhanced security by simplifying the handshake process and removing outdated cryptographic algorithms. The industry is continually pushing for the deprecation of older, less secure protocols to ensure that the baseline level of encryption remains robust against increasingly sophisticated attacks.
Emerging threats, such as quantum computing, pose a long-term challenge to current cryptographic standards. Quantum computers have the potential to break existing public-key encryption algorithms, necessitating the development of "post-quantum cryptography." Researchers are actively working on new algorithms that can withstand quantum attacks, ensuring that secure communication remains viable in a post-quantum world. This research is critical for protecting sensitive data, including government secrets and financial transactions, far into the future.
Another trend is the move towards "HTTPS Everywhere" – a collective effort to encrypt all web traffic by default. Initiatives like Let's Encrypt have made it easier and free for website owners to obtain SSL/TLS certificates, accelerating the adoption of HTTPS across millions of websites. This widespread implementation helps to eliminate mixed content warnings and creates a more uniformly secure internet, making it harder for attackers to find weak points.
Furthermore, browser vendors are continuously enhancing their security features, including stricter warnings for insecure sites, improved certificate transparency mechanisms, and the development of new protocols like DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH), which encrypts DNS queries to prevent eavesdropping on domain lookups. These advancements aim to make the internet inherently safer, reducing the burden on individual users to constantly verify connection security.
The journey towards a fully secure internet is ongoing. While HTTPS provides a strong foundation, the continuous innovation in cryptography, the proactive fight against new vulnerabilities, and the collaborative efforts of the tech community are all vital in ensuring that our online interactions, from browsing a simple "https qu ax txvtq mp4" to conducting high-stakes financial transactions, remain protected against the threats of tomorrow.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Security Measures and Best Practices
While understanding HTTPS and recognizing the lock icon are fundamental, a truly secure online experience often requires going beyond the basics. For both individuals and organizations, adopting advanced security measures and best practices is crucial to building a robust defense against the myriad of cyber threats that exist today.
For individual users, this includes:
- Using Strong, Unique Passwords: A strong password policy, ideally enforced with a password manager, is non-negotiable. Reusing passwords across multiple sites significantly increases your risk.
- Enabling Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security, such as a code from your phone or a physical security key, can prevent unauthorized access even if your password is compromised. This is especially important for critical accounts like your email, banking, and social media.
- Keeping Software Updated: Regularly updating your operating system, web browser, and all applications ensures you have the latest security patches against known vulnerabilities.
- Being Wary of Phishing Attempts: Always double-check the URL of a website, especially before entering login credentials or personal information. Phishing sites often mimic legitimate ones but will lack the proper HTTPS certificate or have subtle URL discrepancies.
- Using a VPN on Public Wi-Fi: While HTTPS encrypts traffic to a specific site, a Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts all your internet traffic, providing an additional layer of security when using untrusted networks like public Wi-Fi.
For website owners and businesses, advanced measures include:
- Implementing HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS): HSTS is a security policy that forces web browsers to interact with a website only over HTTPS, even if the user types "http://" or clicks on an HTTP link. This prevents downgrade attacks and ensures that all connections are secure.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Proactively identifying and fixing vulnerabilities in web applications and infrastructure is vital.
- Content Security Policy (CSP): CSP helps mitigate cross-site scripting (XSS) and other code injection attacks by specifying which dynamic resources are allowed to load on a page.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): WAFs provide an additional layer of protection by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between a web application and the internet, blocking malicious requests.
- Employee Training: Human error remains a significant vulnerability. Educating employees about phishing, social engineering, and secure browsing habits is paramount.
Ultimately, a holistic approach to cybersecurity, combining robust technical implementations like HTTPS with vigilant user practices and continuous education, is the most effective way to navigate the complexities of the digital world securely. Whether you're a casual browser or a large enterprise, embracing these advanced security measures is key to protecting your data and maintaining trust in the online ecosystem.
Conclusion
From the moment you connect to a webpage, whether it's to watch a video like "https qu ax txvtq mp4" or to manage your sensitive financial data, the silent guardian of your online privacy is HTTPS. We've explored how this critical protocol, powered by TLS encryption, forms the backbone of secure communication over a computer network, ensuring that your data remains confidential, authentic, and untampered. The ubiquitous lock icon in your browser URL bar is not just a symbol; it's a testament to the intricate processes that protect your digital interactions, preventing eavesdropping and verifying the identity of the websites you visit.
We've seen how HTTPS is not only a technical necessity but also a strategic imperative for website owners, influencing everything from Google's search rankings to the accuracy of your analytics data. Its widespread adoption, championed by major tech companies like Google and Microsoft, has transformed the internet into a more trustworthy environment. As we look to the future, the continuous evolution of encryption standards and the ongoing battle against emerging cyber threats underscore the enduring importance of HTTPS as our primary digital shield.
Now that you understand the power of HTTPS, make it a habit to check for that lock icon. Be vigilant about "Not Secure" warnings, and empower yourself with knowledge about online safety. Share this article with friends and family to spread awareness about secure browsing. What are your thoughts on the importance of HTTPS in daily online activities? Leave a comment below and let us know! For more insights into cybersecurity and digital best practices, explore other articles on our site.
What Is HTTPS? Secure Browsing and Sharing - Panda Security

HTTP vs HTTPS: What’s the Difference Between the HTTP and HTTPS
HTTP vs HTTPS: Comparison, Pros and Cons, and More